GRACEVIT

The product information provided in this page is intended only for the selected country.
Gracevit contains sitafloxacin hydrate as an active ingredient, and is clinically effective in severe cases of bacterial infection where resistant bacteria are the suspected cause. This medication belongs to a class of drugs known as quinolone antibiotics and works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria. It is usually used to treat a wide range of infections including skin, respiratory, urinary tract, gynaecologic, otologic and dental infections.
Gracevit Tab 50 can be used for infections caused by the following bacteria: Sitafloxacin-susceptible Staphylococcus sp., Streptococcus sp., Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterococcus sp., Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis, Escherichia coli, Citrobacter sp., Klebsiella sp., Enterobacter sp., Serratia sp., Proteus sp., Morganella morganii, Haemophilus influenzae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Legionella pneumophila, Peptostreptococcus sp., Prevotella sp., Porphyromonas sp., Fusobacterium sp., Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydophila (Chlamydia) pneumoniae and Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
Laryngopharyngitis, tonsillitis (including peritonsillitis and peritonsillar abscess), acute bronchitis, pneumonia, and secondary infection of chronic respiratory diseases; Cystitis, pyelonephritis, and urethritis; Cervicitis; Otitis media and sinusitis; Periodontitis, pericoronitis, and osteitis of jaw.
Precaution for indications: Gracevit Tab 50 should be used in consideration for benefit-risk balance since a high incidence of diarrhea and loose stools has been observed. (See Adverse Reactions.)
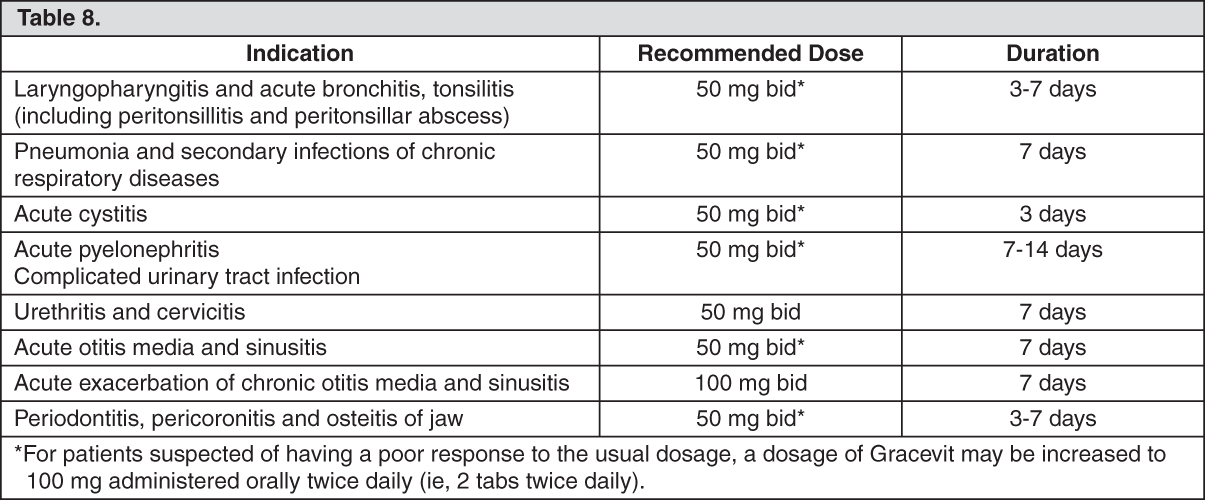
Adult: Usual Dose: 50 mg administered orally twice daily (ie, 1 tab twice daily). (See Table 8.)
Precautions for Dosage and Administration: As a general rule, the susceptibility of the causative bacteria to Gracevit should be confirmed and the duration of administration of Gracevit should be limited to the minimum period required for the treatment of the patient’s condition, in order to prevent the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Higher blood levels of sitafloxacin have been noted following administration in patients with renal impairment; therefore, the dosage and dosing interval of Gracevit should be adjusted when used in this population. (See Pharmacokinetics under Actions.)
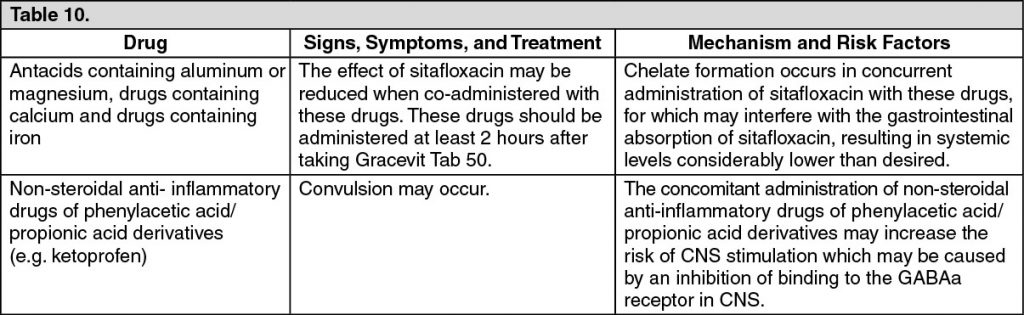
Gracevit should be taken at least 2 hrs before taking antacids containing aluminum or magnesium and drugs containing calcium and iron since the effect of sitafloxacin may be reduced when co-administered with these drugs.
Phototoxicity was observed after exposure to ultraviolet irradiation in subjects orally administered with sitafloxacin 500 mg once or twice daily. The QT interval was prolonged in a dose-dependent manner with a mean fluctuation range of 10 msec or less, following intravenous administration of sitafloxacin 400 to 800 mg twice daily.
Gracevit Tab 50 is contraindicated in the following patients: Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any ingredients of Gracevit Tab 50 or other quinolones.
Pregnant women or women suspected of being pregnant (See Use in Pregnancy & Lactation).
Pediatric patients (See Pharmacology: Toxicology: Preclinical Safety Data under Actions): The safety of Gracevit Tab 50 in low birth weight infants, newborn infants, infants and toddlers, children and adolescents has not been established.
Gracevit Tab 50 must not be used in pregnant women or women suspected of being 169 pregnant. [The safety of the product in these populations has not been established.]
Nursing mothers must be guided to avoid the breast-feeding during treatment with Gracevit Tab 50. [Preclinical studies showed that sitafloxacin is excreted into milk in rats.]
Adult: Usual Dose: 50 mg administered orally twice daily (ie, 1 tab twice daily). (See Table 8.)

Precautions for Dosage and Administration: As a general rule, the susceptibility of the causative bacteria to Gracevit should be confirmed and the duration of administration of Gracevit should be limited to the minimum period required for the treatment of the patient’s condition, in order to prevent the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Higher blood levels of sitafloxacin have been noted following administration in patients with renal impairment; therefore, the dosage and dosing interval of Gracevit should be adjusted when used in this population. (See Pharmacokinetics under Actions.)
Gracevit should be taken at least 2 hrs before taking antacids containing aluminum or magnesium and drugs containing calcium and iron since the effect of sitafloxacin may be reduced when co-administered with these drugs.
Careful Administration (Gracevit Tab 50 should be administered with caution in the following patients): Patients with renal impairment [Persistent increased serum sitafloxacin concentration has been reported in patients with renal impairment (See Pharmacology: Pharmacokinetics under Actions)].
Patients with convulsive diseases such as epilepsy or with a history of convulsive diseases [Convulsion in association with the use of the other quinolones has been reported].
Patients with myasthenia gravis [Exacerbation of myasthenia gravis in associated with the use of the other quinolones has been reported].
Patients complicated with aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection, or patients who have a previous history, positive family history, or risk factors (Marfan syndrome, etc.) of aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection [The increased risk of aortic aneurysm and dissection after intake of fluoroquinolones have been reported in overseas epidemiologic studies (see “Important Precautions” and “Clinically significant adverse reactions” as follows)].
Elderly patients [Since elderly patients generally have reduced physiological function, Gracevit Tab 50 should be used with caution while closely observation of the patient’s condition (See Pharmacology: Pharmacokinetics under Actions)].
Important Precautions: Aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection may occur; therefore, patients should be 96 carefully observed and instructed to seek medical attention immediately if they experience symptoms, e.g., in case of pain in the abdomen, chest, or back. Imaging assessment should be considered if necessary for patients complicated with aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection, or patients who have a previous history, positive family history, or risk factors of aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection (see “Careful Administration” in previous text and “Clinically significant adverse reactions” in the following text).
Clinically significant adverse reactions: Shock, Anaphylaxis (incidence unknown Note1): Since shock or anaphylaxis may occur, patients should be carefully observed and if any abnormality is observed, such as blood pressure reductions, dyspnea, rash, or angioedema etc., Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate measure taken.
Mucocutaneous ocular syndrome (Stevens-Johnson syndrome) (incidence unknownNote1): Since mucocutaneous ocular syndrome may occur, patients should be carefully observed and if any signs of abnormality are noted, Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate treatment measure taken.
Acute renal failure (incidence unknown Note1): Since acute renal failure has been reported with the use of sitafloxacin. Patients should be carefully observed and if any abnormal symptoms occur in a patient being treated with Gracevit Tab 50, Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate measure taken.
Hepatic function disorders (incidence <0.1%): Since hepatic function disorders, including increased AST (GOT) and increased ALT (GPT), have been reported with the use of Gracevit Tab 50, patients should be carefully observed and if any abnormal symptoms occur in a patient being treated with Gracevit Tab 50, Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate measure taken.
Thrombocytopenia (incidence unknownNote1): Since thrombocytopenia has been reported with the use of Gracevit Tab 50, patients should be carefully observed and if any abnormal symptoms occur in a patient being treated with Gracevit Tab 50, Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate measure taken.
Pseudomembranous colitis (incidence unknown Note1): Since pseudomembranous colitis may occur. If such symptoms as abdominal pain and frequent diarrhea are noted, Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate measure taken.
Hypoglycemia (incidence <0.1%): Since hypoglycemia, and sometimes hypoglycemic coma, have been reported with the use of sitafloxacin. Patients should be carefully observed and if any abnormal symptoms occur in a patient being treated with Gracevit Tab 50, Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate measure taken. Hypoglycemia may be prone to develop in patients with diabetes mellitus, patients with impaired renal function and elderly patients.
Psychiatric symptoms such as confusion, delirium and hallucination (incidence unknown Note1): Since psychiatric symptoms such as confusion, delirium, and hallucination have been reported with the use of Gracevit Tab 50, patients should be carefully observed and if any abnormal symptoms occur in a patient being treated with Gracevit Tab 50, Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate measure taken.
Aortic aneurysm, aortic dissection (incidence unknown Note 2): Aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection may occur. If any abnormalities are observed, appropriate medical treatment should be taken (see “Careful Administration” and “Important Precautions” in previous text).
Note1: The incidence of adverse reactions is unknown as the adverse reaction is that which has been reported spontaneously.
Note2: The incidence of adverse reactions is unknown as these adverse reactions are those which have been reported from overseas epidemiologic studies.
Precautions concerning use: Precaution regarding dispensing: When Gracevit Tab 50 is dispensed, patients should be instructed to remove each tablet from the PTP blister package before taking the drug. (It has been reported that accidental ingestion of the blister package can lead to esophageal mucosal injury and subsequent perforation caused by the pointed corner of the package, resulting in serious complications such as mediastinitis.)
Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines: Some undesirable effects (e.g. dizziness or vertigo), which may affect the ability to drive or operate machinery, have been reported uncommonly (less than 1.0%). Sitafloxacin may have some influence on the ability to drive and use machine.
In clinical trials conducted in Japan, adverse drug reactions (including abnormal changes in laboratory tests) were reported 409 patients (33.5%) out of 1,220 patients. The frequently reported adverse drug reactions were diarrhea 69 patients (5.7%), loose stools 86 patients (7.0%), headache 26 patients (2.1%), increased ALT (GPT) 72 patients (5.9%), increased AST (GOT) 59 patients (4.8%), increased eosinophil count 47 patients (3.9%), and others.
(At the supplemental approval of “dose and administration” in August 2011)
In the post-marketing study (conducted between December 2008 and November 2010 in Japan), adverse drug reactions (including abnormal changes in laboratory tests) were reported in 148 patients (4.4%) out of 3,331 patients. The frequently reported adverse drug reactions were diarrhea 41 patients (1.2%), loose stools 14 patients (0.4%), increased ALT(GPT) 22 patients (0.7%), increased AST(GOT) 16 patients (0.5%) and rash 12 patients (0.4%), and others.
(At the end of the post-marketing study)
The following adverse reactions have been reported in pre-approval clinical trials and clinical trials for supplemental NDA and in post-marketing experience including a post-marketing study. If any abnormal event is noted, appropriate measures, such as discontinuing treatment, should be taken as needed.
The frequency of adverse drug reactions based on the exposure to sitafloxacin in total of 4,551 patients in pooled Phase 3 clinical studies (Phase 3 clinical studies for the initial NDA and for the supplemental NDA) and a post-marketing study is reflected.
The following CIOMS frequency rating is used: Very common: 10% ≤ incidence; Common: 1% ≤ incidence < 10%; Uncommon: 0.1% ≤ incidence < 1%; Rare: 0.01% ≤ incidence < 0.1%; Very rare: incidence < 0.01%; Unknown (cannot be estimated from the available data).
*: see Clinically significant adverse reactions in previously mentioned text, each incidence is based on serious events.
Infections and infestations: Rare: vaginal candidiasis.
Immune system disorders: Unknown: anaphylaxis*.
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Rare: hypoglycemia (hypoglycemic coma may occur)*.
Psychiatric disorders: Rare: insomnia.
Unknown: confusion*, delirium*, hallucination*.
Nervous system disorders: Uncommon: headache, dizziness.
Vascular disorders: Unknown: shock*.
Gastrointestinal disorders: Common: diarrhea, loose stools.
Uncommon: abdominal pain, abdominal distension, constipation, dyspepsia, abdominal discomfort stomatitis, nausea.
Rare: cheilitis, frequent bowel movements, glossitis, vomiting, oral paraesthesia.
Unknown: pseudomembranous colitis*.
Hepatobiliary disorders: Uncommon: hepatic function disorders*.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Uncommon: rash.Rare: pruritus, urticaria.
Unknown: mucocutaneous ocular syndrome (Stevens-Johnson syndrome)*, photosensitivity.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Rare: back pain.
Renal and urinary disorders: Unknown: acute renal failure*.
General disorders and administration site conditions: Rare: chills, abnormal feeling, thirst, malaise.
Unknown: edema.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Unknown: thrombocytopenia*.
Investigations: Common: increased ALT (GPT), increased AST (GOT), increased eosinophil count.
Uncommon: increased γ-GTP, increased LDH, increased triglycerides, increased ALP, increased blood potassium, decreased neutrophil count, increased platelet count, decreased white blood cell count, increased CK (CPK), decreased blood sugar, positive urinary protein.
Rare: decreased blood potassium, increased white blood cell count.
Clinically significant adverse reactions reported in association with the use of other quinolones: The following clinically significant adverse reactions have been reported in association with the use of the other quinolones. Therefore, careful monitoring of patients being treated with Gracevit Tab 50 is recommended. The drug should be discontinued if any abnormal symptoms related to the events occur, and appropriate therapies should be initiated immediately.
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN); convulsions; QT prolongation, ventricular tachycardia (including Torsades de pointes); Jaundice; Interstitial pneumonia; Rhabdomyolysis; Tendon disorders; Agranulocytosis; Pancytopenia; Hemolytic anemia; Exacerbation of myasthenia gravis.
Gracevit Tab 50 should be co-administered with care when administered with the following drugs (see Table 10).
Incompatibilities: Not applicable.
STORAGE: Special Precaution for Storage: Store below 30°C.
Shelf-Life: 48 months.
One tablet contains Sitafloxacin hydrate 53.3 mg equivalence to Sitafloxacin 50 mg.
Sitafloxacin occurs as pale yellowish white to yellowish white crystals or crystalline powder. It is sparingly soluble in phosphoric acid test solution (consisting of 50 g phosphoric acid dissolved in 950 mL water), slightly soluble in 0.1 mol/L hydrochloric acid test solution, acetonitrile and methanol, very slightly soluble in ethanol (99.5), and practically insoluble in water. It appears as light yellowish brownish white depending on lighting conditions.
Sitafloxacin hydrate is (-)-7-[(7S)-7-Amino-5-azaspiro[2.4]hept-5-yl]-8-chloro-6-fluoro-1-[(1R,2S)-2-fluorocyclopropyl]-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid.
Molecular Formula: C19H18ClF2N3O3.
Molecular Weight: 409.81.
Melting Point: 217-223°C.
Distribution Coefficient: 1-octanol/water at 25°C; 0.244. (See Table 1.)
Excipients/Inactive Ingredients: D-mannitol (JP), corn starch (JP), low substituted hydroxypropylcellulose (JP), hydroxypropylcellulose (JP), magnesium stearate (JP), hypromellose (JP), titanium oxide (JP), talc (JP), macrogol 6000 (JP), polydimethylsiloxane and silicon dioxide mixture (JPE), carnauba wax (JP).(JP): The Japanese Pharmacopoeia, (JPE): Japanese Pharmaceutical Excipients.
Pharmacology: Pharmacodynamics: Mechanism of Action: The mechanism of action of sitafloxacin involves inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. Bactericidal activity of sitafloxacin results from inhibition of these enzymes. The inhibitory activity of sitafloxacin against these enzymes was higher than that of the other quinolone antimicrobials used as comparators. Sitafloxacin also has a potent inhibitory activity against enzymes from quinolone-resistant bacteria.
Antibacterial Activity: Sitafloxacin has a broad spectrum of antibacterial activity against aerobic and anaerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, as well as atypical bacteria. Sitafloxacin showed potent antibacterial activities against microorganisms such as Staphylococcus sp., Streptococcus sp., Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterococcus sp., Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis, Escherichia coli, Citrobacter sp., Klebsiella sp., Enterobacter sp., Serratia sp., Proteus sp., Morganella morganii, Haemophilus influenzae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Legionella pneumophila, Peptostreptococcus sp., Prevotella sp., Porphyromonas sp., Fusobacterium sp., Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydophila (Chlamydia) pneumoniae, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. In comparison to other quinolone antimicrobials, sitafloxacin shows more potent antibacterial activities in particular against Streptococcus pneumoniae (including penicillin-resistant and macrolide-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae), Enterococcus sp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli (including quinolone-resistant Escherichia coli).
Therapeutic Effects of Sitafloxacin for Experimental Infection: Sitafloxacin showed a therapeutic effect against infection, reflecting its antimicrobial activity in vitro in mouse models of sepsis caused by Gram-positive or Gram-negative organisms. Sitafloxacin also showed a greater therapeutic effect than the other quinolone antimicrobial agents used as controls in a mouse model of pneumococcal respiratory tract infection.
Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Analysis in Patients with Respiratory Infections: The results of the PK/PD analysis in a clinical study conducted in patients with respiratory tract infections demonstrated that the eradication rate of causative pathogens increased along with increase of AUC0-24hr/MIC or Cmax/MIC value. The rate of disappearance of major causative organisms in patients with respiratory tract infections, involving 22 Streptococcus pneumoniae strains, was 96.3% (78/81) for cases with an AUC0-24hr/MIC of more than 100 or 96.3% (79/82) for cases with a Cmax/MIC of more than 5. The results of clinical studies conducted in patients with respiratory tract infections due to Streptococcus pneumonia strains, demonstrated that the eradication rates of the pathogens were both 98.9% (89/90) in case with an ƒAUC0-24hr/MIC greater than 30 and in case with an ƒCpeak/MIC greater than 2, as estimated for the serum concentration of unbinding form of sitafloxacin, respectively.
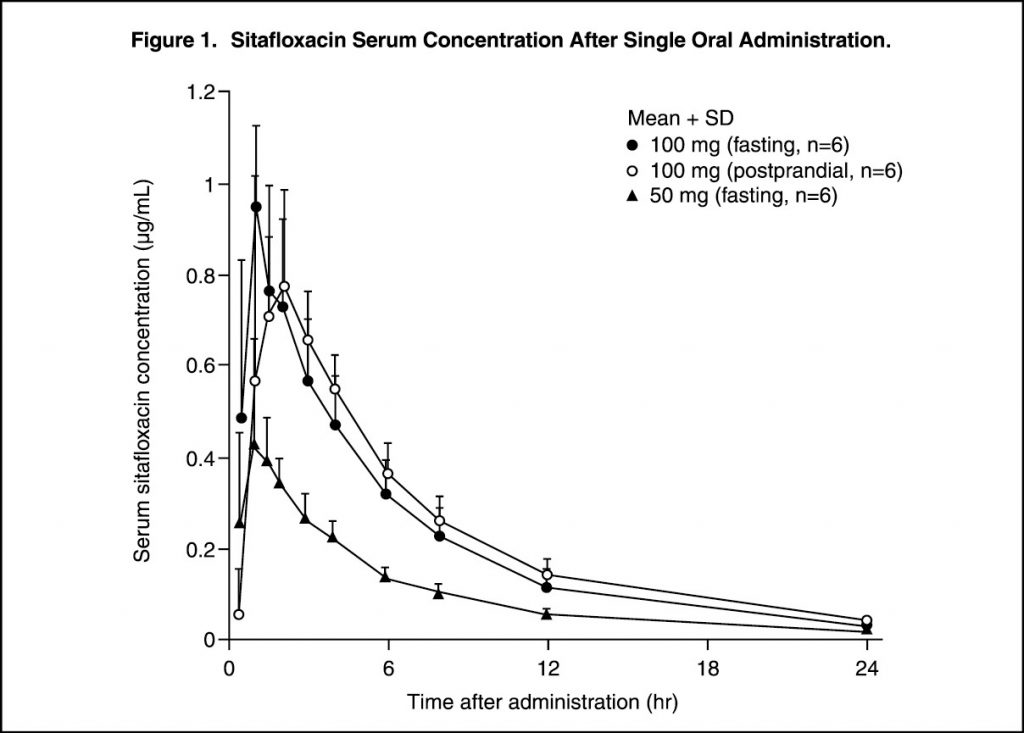
Pharmacokinetics: Serum Drug Concentrations: The following figures and tables show serum concentrations and pharmacokinetic parameters of sitafloxacin following a single and repeated oral dose administered to healthy adults in the fasting or postprandial state. (See Figures 1, 2 and 3; and Tables 2, 3 and 4.)
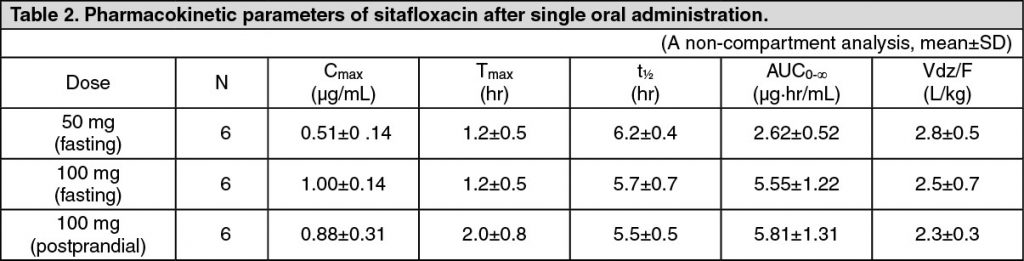
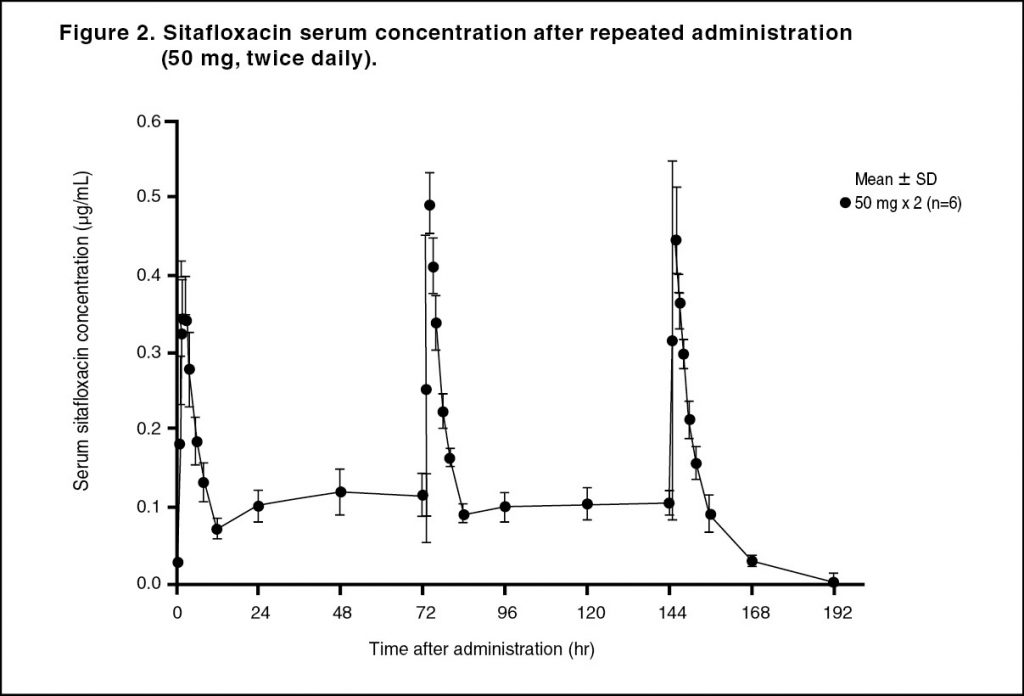
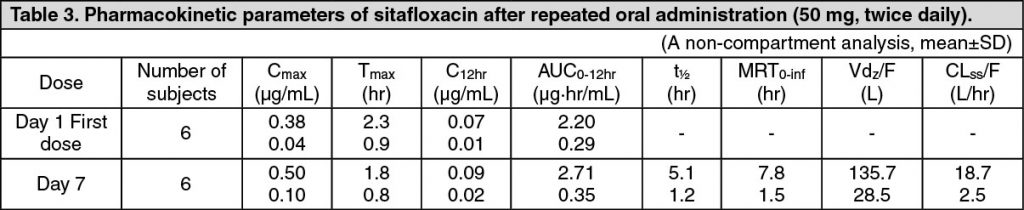
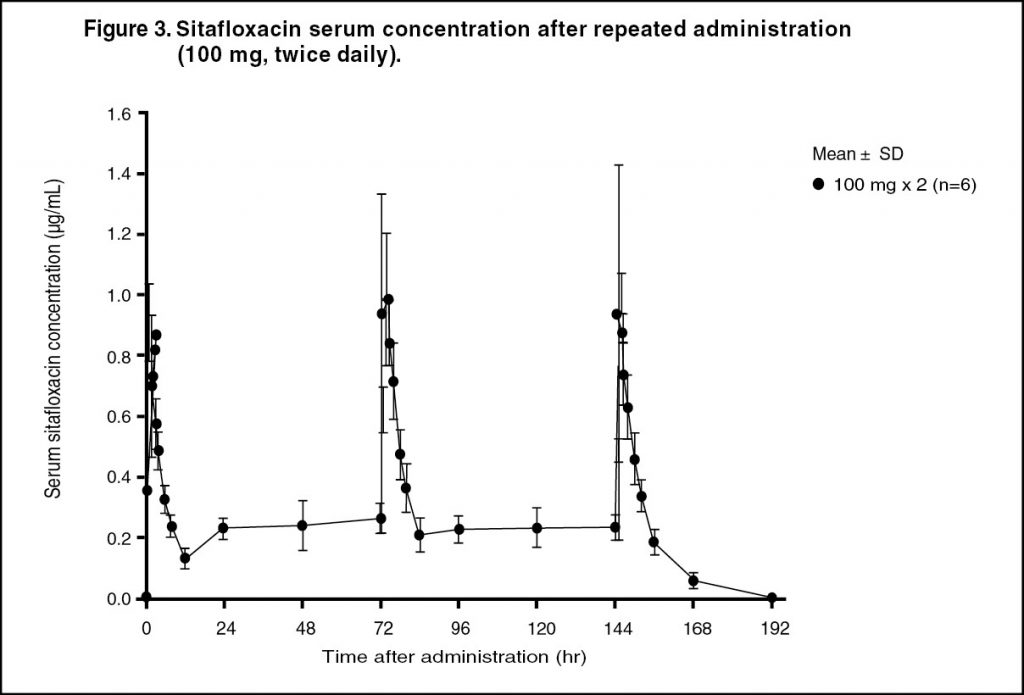
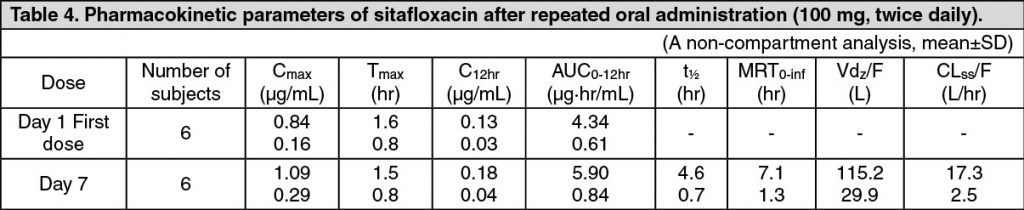
Serum Protein Binding: The mean serum protein-binding rate of sitafloxacin was practically constant ranging from 46-55%, as determined by ultrafiltration, 1, 4 and 8 hours after being administered orally to healthy adults in a single dose of 100 mg.
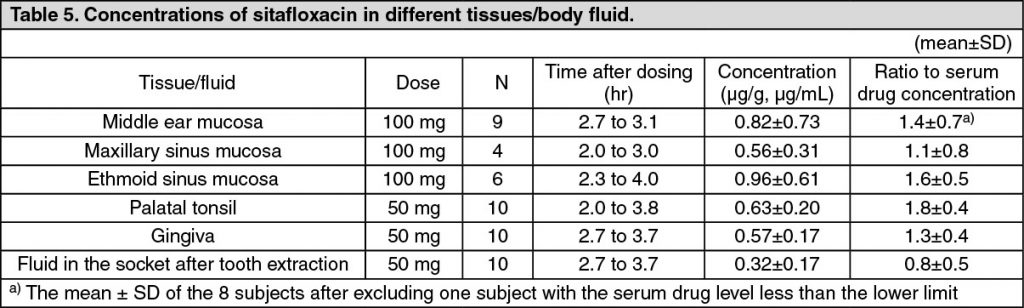
Distribution: When sitafloxacin was administered orally in a single dose of 50 or 100 mg, the drug concentrations in different tissue and body fluid were as follows, indicating favorable drug transfer to these tissue/fluid: see Table 5.
Metabolism: Sitafloxacin was scarcely metabolized and was excreted as an unchanged form in the urine. Some of the metabolites identified in the serum, urine and feces are as follows: glucuronide, 7′-oxo metabolite, 7′S-hydroxylated metabolite, glucuronide of 7′S-hydroxylated metabolite, and N-acetyl conjugate.
An in vitro study performed using human tissue specimens showed that sitafloxacin modestly inhibited the CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 enzymatic activities, but did not cause any inhibition of other CYP isoforms eg, CYP2C9, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4.
Excretion: When 50 or 100 mg of sitafloxacin was administered to healthy adults in the fasting state, approximately 70% of these administered doses was excreted in unchanged form in urine within 48 hours.
Data of the United Kingdom showed that after administration of 14C-labeled sitafloxacin at a dose of 100 mg, approximately 80% of the administered radioactivity was excreted in urine within 72 hours and approximately 20% was excreted in feces within 72 hours.
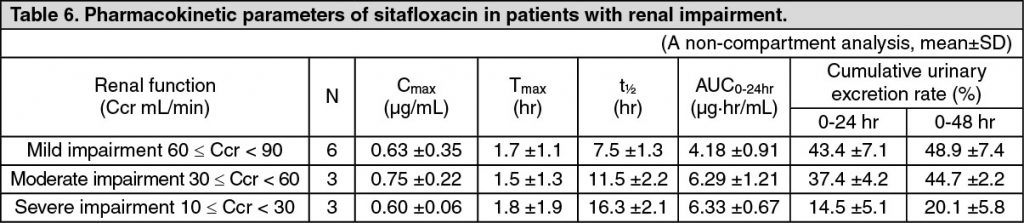
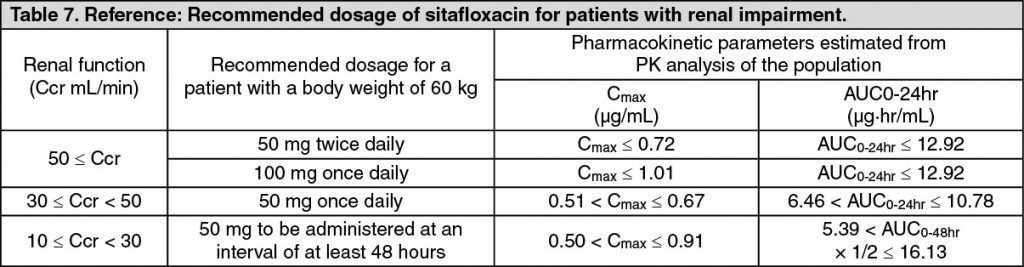
Pharmacokinetics in Patients with Renal Function Disorders: In patients grouped according to creatinine clearance value (Ccr) who were administered a single oral dose of 50 mg sitafloxacin in the fasted state, a prolonged biological half-life of serum concentration and a delay of the urinary excretion were observed progressively with decreasing renal function. (See Tables 6 and 7.)
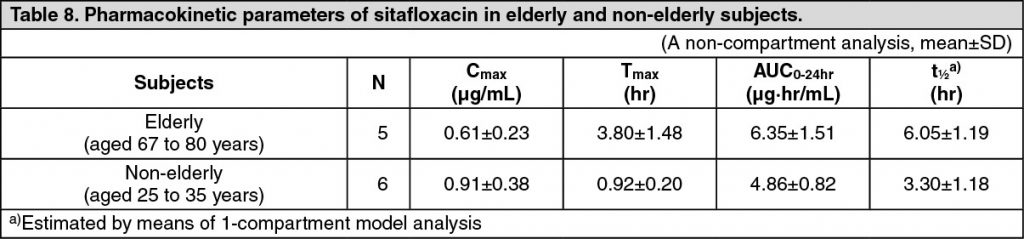
Pharmacokinetics in Elderly Subjects: Five elderly and 6 non-elderly subjects aged from 67 to 80 years and from 25 to 35 years, respectively, received a single oral dose of 100 mg of sitafloxacin in the fasting state. In the elderly subjects, prolonged t½ decreased Cmax and increased AUC0-24hr were observed in comparison to the non-elderly subjects. These findings suggest that the pharmacokinetic profile of sitafloxacin is influenced by age-related decline of the absorption and excretion functions. (See Table 8.)
Toxicology: Preclinical Safety Data: Single-Dose Toxicity: Approximate oral lethal doses were over 1880 and 469 mg/kg in rats and monkeys, respectively. Intravenous LD50 was 188 mg/kg in mice.
Repeated-Dose Toxicity: In rats, toxic findings included urinary medicine-like crystals with no renal lesions, and exacerbation of spontaneous femoral osteochondrotic lesions after 4 and 13-week oral dosing, with 46.9 and 20 mg/kg/day of No Observed Adverse Effect Level (NOAEL). In monkeys, decreased spermatogenic cells in testis, and a mild increase in serum phospholipid level were seen after 4 and 52-week oral dosing, with 28.1 and 25 mg/kg/day of NOAEL.
Genotoxicity: Sitafloxacin was positive in in vitro reverse mutation (Escherichia coli WP2uvrA/pKM101), chromosomal aberration and mouse lymphoma TK tests, but negative in in vivo micronucleus, unscheduled DNA synthesis and dominant lethality tests.
Reproductive Toxicity: Sitafloxacin had no effects on fertility, pregnancy and lactation in parental rats, but induced abortion in rabbits as a common effect of antibiotics. Sitafloxacin was not teratogenic in rats and rabbits although minor effects were noted in foetuses and offsprings.
Arthrotoxicity in dogs: Sitafloxacin induced blister formation in the articular cartilage of juvenile, but not adult, dogs.
Phototoxicity: NOAELs were 20 and 93.8 mg/kg/day in albino and pigmented mice.
Photogenotoxicity: Sitafloxacin was positive in in vitro photogenotoxicity test, but NOAEL was 20 mg/kg in in vivo mouse test.
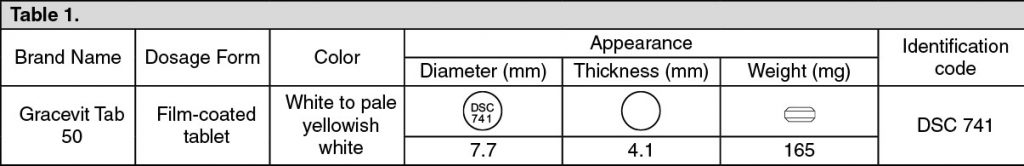
FC tab 50 mg (white to pale yellowish white, round, biconvex with DSC 741 printed on one side) x 10’s.
Gracevit Tab 50 can be used for infections caused by the following bacteria: Sitafloxacin-susceptible Staphylococcus sp., Streptococcus sp., Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterococcus sp., Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis, Escherichia coli, Citrobacter sp., Klebsiella sp., Enterobacter sp., Serratia sp., Proteus sp., Morganella morganii, Haemophilus influenzae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Legionella pneumophila, Peptostreptococcus sp., Prevotella sp., Porphyromonas sp., Fusobacterium sp., Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydophila (Chlamydia) pneumoniae and Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
Laryngopharyngitis, tonsillitis (including peritonsillitis and peritonsillar abscess), acute bronchitis, pneumonia, and secondary infection of chronic respiratory diseases; Cystitis, pyelonephritis, and urethritis; Cervicitis; Otitis media and sinusitis; Periodontitis, pericoronitis, and osteitis of jaw.
Precaution for indications: Gracevit Tab 50 should be used in consideration for benefit-risk balance since a high incidence of diarrhea and loose stools has been observed. (See Adverse Reactions.)
Copyright MIMS
Adult: Usual Dose: 50 mg administered orally twice daily (ie, 1 tab twice daily). (See Table 8.)

Precautions for Dosage and Administration: As a general rule, the susceptibility of the causative bacteria to Gracevit should be confirmed and the duration of administration of Gracevit should be limited to the minimum period required for the treatment of the patient’s condition, in order to prevent the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Higher blood levels of sitafloxacin have been noted following administration in patients with renal impairment; therefore, the dosage and dosing interval of Gracevit should be adjusted when used in this population. (See Pharmacokinetics under Actions.)
Gracevit should be taken at least 2 hrs before taking antacids containing aluminum or magnesium and drugs containing calcium and iron since the effect of sitafloxacin may be reduced when co-administered with these drugs.
Copyright MIMS
Phototoxicity was observed after exposure to ultraviolet irradiation in subjects orally administered with sitafloxacin 500 mg once or twice daily. The QT interval was prolonged in a dose-dependent manner with a mean fluctuation range of 10 msec or less, following intravenous administration of sitafloxacin 400 to 800 mg twice daily.
Copyright MIMS
Gracevit Tab 50 is contraindicated in the following patients: Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any ingredients of Gracevit Tab 50 or other quinolones.
Pregnant women or women suspected of being pregnant (See Use in Pregnancy & Lactation).
Pediatric patients (See Pharmacology: Toxicology: Preclinical Safety Data under Actions): The safety of Gracevit Tab 50 in low birth weight infants, newborn infants, infants and toddlers, children and adolescents has not been established.
Copyright MIMS
Gracevit Tab 50 must not be used in pregnant women or women suspected of being 169 pregnant. [The safety of the product in these populations has not been established.]
Nursing mothers must be guided to avoid the breast-feeding during treatment with Gracevit Tab 50. [Preclinical studies showed that sitafloxacin is excreted into milk in rats.]
Copyright MIMS
Adult: Usual Dose: 50 mg administered orally twice daily (ie, 1 tab twice daily). (See Table 8.)

Precautions for Dosage and Administration: As a general rule, the susceptibility of the causative bacteria to Gracevit should be confirmed and the duration of administration of Gracevit should be limited to the minimum period required for the treatment of the patient’s condition, in order to prevent the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Higher blood levels of sitafloxacin have been noted following administration in patients with renal impairment; therefore, the dosage and dosing interval of Gracevit should be adjusted when used in this population. (See Pharmacokinetics under Actions.)
Gracevit should be taken at least 2 hrs before taking antacids containing aluminum or magnesium and drugs containing calcium and iron since the effect of sitafloxacin may be reduced when co-administered with these drugs.
Copyright MIMS
Careful Administration (Gracevit Tab 50 should be administered with caution in the following patients): Patients with renal impairment [Persistent increased serum sitafloxacin concentration has been reported in patients with renal impairment (See Pharmacology: Pharmacokinetics under Actions)].
Patients with convulsive diseases such as epilepsy or with a history of convulsive diseases [Convulsion in association with the use of the other quinolones has been reported].
Patients with myasthenia gravis [Exacerbation of myasthenia gravis in associated with the use of the other quinolones has been reported].
Patients complicated with aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection, or patients who have a previous history, positive family history, or risk factors (Marfan syndrome, etc.) of aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection [The increased risk of aortic aneurysm and dissection after intake of fluoroquinolones have been reported in overseas epidemiologic studies (see “Important Precautions” and “Clinically significant adverse reactions” as follows)].
Elderly patients [Since elderly patients generally have reduced physiological function, Gracevit Tab 50 should be used with caution while closely observation of the patient’s condition (See Pharmacology: Pharmacokinetics under Actions)].
Important Precautions: Aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection may occur; therefore, patients should be 96 carefully observed and instructed to seek medical attention immediately if they experience symptoms, e.g., in case of pain in the abdomen, chest, or back. Imaging assessment should be considered if necessary for patients complicated with aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection, or patients who have a previous history, positive family history, or risk factors of aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection (see “Careful Administration” in previous text and “Clinically significant adverse reactions” in the following text).
Clinically significant adverse reactions: Shock, Anaphylaxis (incidence unknown Note1): Since shock or anaphylaxis may occur, patients should be carefully observed and if any abnormality is observed, such as blood pressure reductions, dyspnea, rash, or angioedema etc., Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate measure taken.
Mucocutaneous ocular syndrome (Stevens-Johnson syndrome) (incidence unknownNote1): Since mucocutaneous ocular syndrome may occur, patients should be carefully observed and if any signs of abnormality are noted, Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate treatment measure taken.
Acute renal failure (incidence unknown Note1): Since acute renal failure has been reported with the use of sitafloxacin. Patients should be carefully observed and if any abnormal symptoms occur in a patient being treated with Gracevit Tab 50, Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate measure taken.
Hepatic function disorders (incidence <0.1%): Since hepatic function disorders, including increased AST (GOT) and increased ALT (GPT), have been reported with the use of Gracevit Tab 50, patients should be carefully observed and if any abnormal symptoms occur in a patient being treated with Gracevit Tab 50, Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate measure taken.
Thrombocytopenia (incidence unknownNote1): Since thrombocytopenia has been reported with the use of Gracevit Tab 50, patients should be carefully observed and if any abnormal symptoms occur in a patient being treated with Gracevit Tab 50, Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate measure taken.
Pseudomembranous colitis (incidence unknown Note1): Since pseudomembranous colitis may occur. If such symptoms as abdominal pain and frequent diarrhea are noted, Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate measure taken.
Hypoglycemia (incidence <0.1%): Since hypoglycemia, and sometimes hypoglycemic coma, have been reported with the use of sitafloxacin. Patients should be carefully observed and if any abnormal symptoms occur in a patient being treated with Gracevit Tab 50, Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate measure taken. Hypoglycemia may be prone to develop in patients with diabetes mellitus, patients with impaired renal function and elderly patients.
Psychiatric symptoms such as confusion, delirium and hallucination (incidence unknown Note1): Since psychiatric symptoms such as confusion, delirium, and hallucination have been reported with the use of Gracevit Tab 50, patients should be carefully observed and if any abnormal symptoms occur in a patient being treated with Gracevit Tab 50, Gracevit Tab 50 should be discontinued and appropriate measure taken.
Aortic aneurysm, aortic dissection (incidence unknown Note 2): Aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection may occur. If any abnormalities are observed, appropriate medical treatment should be taken (see “Careful Administration” and “Important Precautions” in previous text).
Note1: The incidence of adverse reactions is unknown as the adverse reaction is that which has been reported spontaneously.
Note2: The incidence of adverse reactions is unknown as these adverse reactions are those which have been reported from overseas epidemiologic studies.
Precautions concerning use: Precaution regarding dispensing: When Gracevit Tab 50 is dispensed, patients should be instructed to remove each tablet from the PTP blister package before taking the drug. (It has been reported that accidental ingestion of the blister package can lead to esophageal mucosal injury and subsequent perforation caused by the pointed corner of the package, resulting in serious complications such as mediastinitis.)
Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines: Some undesirable effects (e.g. dizziness or vertigo), which may affect the ability to drive or operate machinery, have been reported uncommonly (less than 1.0%). Sitafloxacin may have some influence on the ability to drive and use machine.
Copyright MIMS
In clinical trials conducted in Japan, adverse drug reactions (including abnormal changes in laboratory tests) were reported 409 patients (33.5%) out of 1,220 patients. The frequently reported adverse drug reactions were diarrhea 69 patients (5.7%), loose stools 86 patients (7.0%), headache 26 patients (2.1%), increased ALT (GPT) 72 patients (5.9%), increased AST (GOT) 59 patients (4.8%), increased eosinophil count 47 patients (3.9%), and others.
(At the supplemental approval of “dose and administration” in August 2011)
In the post-marketing study (conducted between December 2008 and November 2010 in Japan), adverse drug reactions (including abnormal changes in laboratory tests) were reported in 148 patients (4.4%) out of 3,331 patients. The frequently reported adverse drug reactions were diarrhea 41 patients (1.2%), loose stools 14 patients (0.4%), increased ALT(GPT) 22 patients (0.7%), increased AST(GOT) 16 patients (0.5%) and rash 12 patients (0.4%), and others.
(At the end of the post-marketing study)
The following adverse reactions have been reported in pre-approval clinical trials and clinical trials for supplemental NDA and in post-marketing experience including a post-marketing study. If any abnormal event is noted, appropriate measures, such as discontinuing treatment, should be taken as needed.
The frequency of adverse drug reactions based on the exposure to sitafloxacin in total of 4,551 patients in pooled Phase 3 clinical studies (Phase 3 clinical studies for the initial NDA and for the supplemental NDA) and a post-marketing study is reflected.
The following CIOMS frequency rating is used: Very common: 10% ≤ incidence; Common: 1% ≤ incidence < 10%; Uncommon: 0.1% ≤ incidence < 1%; Rare: 0.01% ≤ incidence < 0.1%; Very rare: incidence < 0.01%; Unknown (cannot be estimated from the available data).
*: see Clinically significant adverse reactions in previously mentioned text, each incidence is based on serious events.
Infections and infestations: Rare: vaginal candidiasis.
Immune system disorders: Unknown: anaphylaxis*.
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Rare: hypoglycemia (hypoglycemic coma may occur)*.
Psychiatric disorders: Rare: insomnia.
Unknown: confusion*, delirium*, hallucination*.
Nervous system disorders: Uncommon: headache, dizziness.
Vascular disorders: Unknown: shock*.
Gastrointestinal disorders: Common: diarrhea, loose stools.
Uncommon: abdominal pain, abdominal distension, constipation, dyspepsia, abdominal discomfort stomatitis, nausea.
Rare: cheilitis, frequent bowel movements, glossitis, vomiting, oral paraesthesia.
Unknown: pseudomembranous colitis*.
Hepatobiliary disorders: Uncommon: hepatic function disorders*.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Uncommon: rash.Rare: pruritus, urticaria.
Unknown: mucocutaneous ocular syndrome (Stevens-Johnson syndrome)*, photosensitivity.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Rare: back pain.
Renal and urinary disorders: Unknown: acute renal failure*.
General disorders and administration site conditions: Rare: chills, abnormal feeling, thirst, malaise.
Unknown: edema.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Unknown: thrombocytopenia*.
Investigations: Common: increased ALT (GPT), increased AST (GOT), increased eosinophil count.
Uncommon: increased γ-GTP, increased LDH, increased triglycerides, increased ALP, increased blood potassium, decreased neutrophil count, increased platelet count, decreased white blood cell count, increased CK (CPK), decreased blood sugar, positive urinary protein.
Rare: decreased blood potassium, increased white blood cell count.
Clinically significant adverse reactions reported in association with the use of other quinolones: The following clinically significant adverse reactions have been reported in association with the use of the other quinolones. Therefore, careful monitoring of patients being treated with Gracevit Tab 50 is recommended. The drug should be discontinued if any abnormal symptoms related to the events occur, and appropriate therapies should be initiated immediately.
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN); convulsions; QT prolongation, ventricular tachycardia (including Torsades de pointes); Jaundice; Interstitial pneumonia; Rhabdomyolysis; Tendon disorders; Agranulocytosis; Pancytopenia; Hemolytic anemia; Exacerbation of myasthenia gravis.
Copyright MIMS
Gracevit Tab 50 should be co-administered with care when administered with the following drugs (see Table 10).

Copyright MIMS
Incompatibilities: Not applicable.
Copyright MIMS
STORAGE: Special Precaution for Storage: Store below 30°C.
Shelf-Life: 48 months.
Copyright MIMS
One tablet contains Sitafloxacin hydrate 53.3 mg equivalence to Sitafloxacin 50 mg.
Sitafloxacin occurs as pale yellowish white to yellowish white crystals or crystalline powder. It is sparingly soluble in phosphoric acid test solution (consisting of 50 g phosphoric acid dissolved in 950 mL water), slightly soluble in 0.1 mol/L hydrochloric acid test solution, acetonitrile and methanol, very slightly soluble in ethanol (99.5), and practically insoluble in water. It appears as light yellowish brownish white depending on lighting conditions.
Sitafloxacin hydrate is (-)-7-[(7S)-7-Amino-5-azaspiro[2.4]hept-5-yl]-8-chloro-6-fluoro-1-[(1R,2S)-2-fluorocyclopropyl]-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid.
Molecular Formula: C19H18ClF2N3O3.
Molecular Weight: 409.81.
Melting Point: 217-223°C.
Distribution Coefficient: 1-octanol/water at 25°C; 0.244. (See Table 1.)

Excipients/Inactive Ingredients: D-mannitol (JP), corn starch (JP), low substituted hydroxypropylcellulose (JP), hydroxypropylcellulose (JP), magnesium stearate (JP), hypromellose (JP), titanium oxide (JP), talc (JP), macrogol 6000 (JP), polydimethylsiloxane and silicon dioxide mixture (JPE), carnauba wax (JP).(JP): The Japanese Pharmacopoeia, (JPE): Japanese Pharmaceutical Excipients.
Copyright MIMS
Pharmacology: Pharmacodynamics: Mechanism of Action: The mechanism of action of sitafloxacin involves inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. Bactericidal activity of sitafloxacin results from inhibition of these enzymes. The inhibitory activity of sitafloxacin against these enzymes was higher than that of the other quinolone antimicrobials used as comparators. Sitafloxacin also has a potent inhibitory activity against enzymes from quinolone-resistant bacteria.
Antibacterial Activity: Sitafloxacin has a broad spectrum of antibacterial activity against aerobic and anaerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, as well as atypical bacteria. Sitafloxacin showed potent antibacterial activities against microorganisms such as Staphylococcus sp., Streptococcus sp., Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterococcus sp., Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis, Escherichia coli, Citrobacter sp., Klebsiella sp., Enterobacter sp., Serratia sp., Proteus sp., Morganella morganii, Haemophilus influenzae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Legionella pneumophila, Peptostreptococcus sp., Prevotella sp., Porphyromonas sp., Fusobacterium sp., Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydophila (Chlamydia) pneumoniae, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. In comparison to other quinolone antimicrobials, sitafloxacin shows more potent antibacterial activities in particular against Streptococcus pneumoniae (including penicillin-resistant and macrolide-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae), Enterococcus sp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli (including quinolone-resistant Escherichia coli).
Therapeutic Effects of Sitafloxacin for Experimental Infection: Sitafloxacin showed a therapeutic effect against infection, reflecting its antimicrobial activity in vitro in mouse models of sepsis caused by Gram-positive or Gram-negative organisms. Sitafloxacin also showed a greater therapeutic effect than the other quinolone antimicrobial agents used as controls in a mouse model of pneumococcal respiratory tract infection.
Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Analysis in Patients with Respiratory Infections: The results of the PK/PD analysis in a clinical study conducted in patients with respiratory tract infections demonstrated that the eradication rate of causative pathogens increased along with increase of AUC0-24hr/MIC or Cmax/MIC value. The rate of disappearance of major causative organisms in patients with respiratory tract infections, involving 22 Streptococcus pneumoniae strains, was 96.3% (78/81) for cases with an AUC0-24hr/MIC of more than 100 or 96.3% (79/82) for cases with a Cmax/MIC of more than 5. The results of clinical studies conducted in patients with respiratory tract infections due to Streptococcus pneumonia strains, demonstrated that the eradication rates of the pathogens were both 98.9% (89/90) in case with an ƒAUC0-24hr/MIC greater than 30 and in case with an ƒCpeak/MIC greater than 2, as estimated for the serum concentration of unbinding form of sitafloxacin, respectively.
Pharmacokinetics: Serum Drug Concentrations: The following figures and tables show serum concentrations and pharmacokinetic parameters of sitafloxacin following a single and repeated oral dose administered to healthy adults in the fasting or postprandial state. (See Figures 1, 2 and 3; and Tables 2, 3 and 4.)






Serum Protein Binding: The mean serum protein-binding rate of sitafloxacin was practically constant ranging from 46-55%, as determined by ultrafiltration, 1, 4 and 8 hours after being administered orally to healthy adults in a single dose of 100 mg.
Distribution: When sitafloxacin was administered orally in a single dose of 50 or 100 mg, the drug concentrations in different tissue and body fluid were as follows, indicating favorable drug transfer to these tissue/fluid: see Table 5.

Metabolism: Sitafloxacin was scarcely metabolized and was excreted as an unchanged form in the urine. Some of the metabolites identified in the serum, urine and feces are as follows: glucuronide, 7′-oxo metabolite, 7′S-hydroxylated metabolite, glucuronide of 7′S-hydroxylated metabolite, and N-acetyl conjugate.
An in vitro study performed using human tissue specimens showed that sitafloxacin modestly inhibited the CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 enzymatic activities, but did not cause any inhibition of other CYP isoforms eg, CYP2C9, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4.
Excretion: When 50 or 100 mg of sitafloxacin was administered to healthy adults in the fasting state, approximately 70% of these administered doses was excreted in unchanged form in urine within 48 hours.
Data of the United Kingdom showed that after administration of 14C-labeled sitafloxacin at a dose of 100 mg, approximately 80% of the administered radioactivity was excreted in urine within 72 hours and approximately 20% was excreted in feces within 72 hours.
Pharmacokinetics in Patients with Renal Function Disorders: In patients grouped according to creatinine clearance value (Ccr) who were administered a single oral dose of 50 mg sitafloxacin in the fasted state, a prolonged biological half-life of serum concentration and a delay of the urinary excretion were observed progressively with decreasing renal function. (See Tables 6 and 7.)


Pharmacokinetics in Elderly Subjects: Five elderly and 6 non-elderly subjects aged from 67 to 80 years and from 25 to 35 years, respectively, received a single oral dose of 100 mg of sitafloxacin in the fasting state. In the elderly subjects, prolonged t½ decreased Cmax and increased AUC0-24hr were observed in comparison to the non-elderly subjects. These findings suggest that the pharmacokinetic profile of sitafloxacin is influenced by age-related decline of the absorption and excretion functions. (See Table 8.)

Toxicology: Preclinical Safety Data: Single-Dose Toxicity: Approximate oral lethal doses were over 1880 and 469 mg/kg in rats and monkeys, respectively. Intravenous LD50 was 188 mg/kg in mice.
Repeated-Dose Toxicity: In rats, toxic findings included urinary medicine-like crystals with no renal lesions, and exacerbation of spontaneous femoral osteochondrotic lesions after 4 and 13-week oral dosing, with 46.9 and 20 mg/kg/day of No Observed Adverse Effect Level (NOAEL). In monkeys, decreased spermatogenic cells in testis, and a mild increase in serum phospholipid level were seen after 4 and 52-week oral dosing, with 28.1 and 25 mg/kg/day of NOAEL.
Genotoxicity: Sitafloxacin was positive in in vitro reverse mutation (Escherichia coli WP2uvrA/pKM101), chromosomal aberration and mouse lymphoma TK tests, but negative in in vivo micronucleus, unscheduled DNA synthesis and dominant lethality tests.
Reproductive Toxicity: Sitafloxacin had no effects on fertility, pregnancy and lactation in parental rats, but induced abortion in rabbits as a common effect of antibiotics. Sitafloxacin was not teratogenic in rats and rabbits although minor effects were noted in foetuses and offsprings.
Arthrotoxicity in dogs: Sitafloxacin induced blister formation in the articular cartilage of juvenile, but not adult, dogs.
Phototoxicity: NOAELs were 20 and 93.8 mg/kg/day in albino and pigmented mice.
Photogenotoxicity: Sitafloxacin was positive in in vitro photogenotoxicity test, but NOAEL was 20 mg/kg in in vivo mouse test.
Copyright MIMS
Copyright MIMS
FC tab 50 mg (white to pale yellowish white, round, biconvex with DSC 741 printed on one side) x 10’s.
Copyright MIMS









